As a music lover, I have often wondered what makes the harmonica sound so magical and unique. How is it that this little instrument can create such beautiful and captivating sounds? I have decided to explore the secrets behind the iconic instrument to uncover what makes the harmonica sound so special.
Anatomy of the Harmonica
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Cover plates | Two metal plates that cover the top and bottom of the harmonica, typically made of metal. |
| Comb | A thin sheet of plastic, wood, or metal that separates the air chambers and channels the air. |
| Reeds | Metal plates that vibrate when air passes over them, producing the sound. |
| Reed plates | Metal plates that hold the reeds in place. |
| Mouthpiece | The part of the harmonica that you blow into to create sound. |
| Buttons | The buttons on the side of the harmonica that control the air flow. |
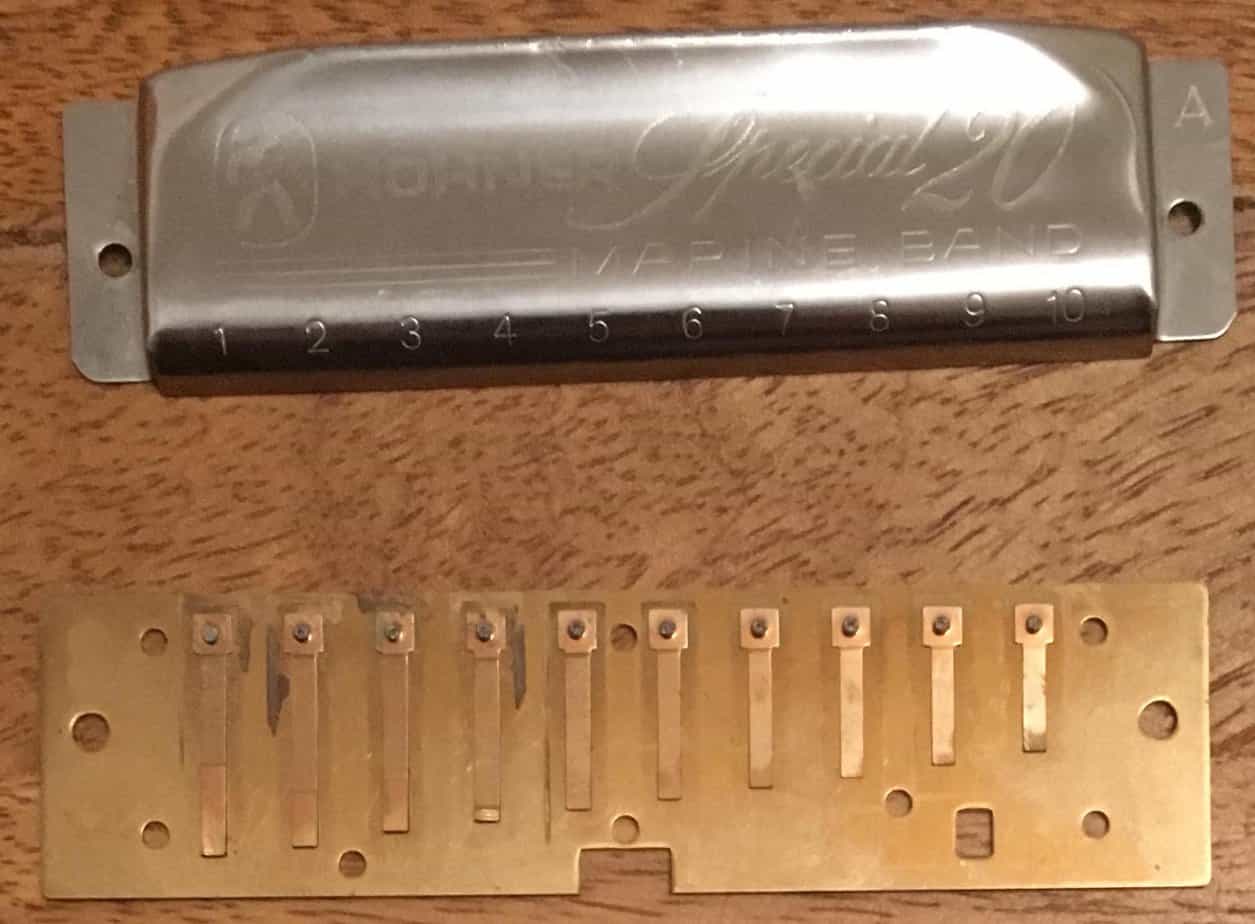
The harmonica is made up of several parts, including cover plates, a comb, reeds, reed plates, a mouthpiece, and buttons. The cover plates cover the top and bottom of the harmonica and are typically made of metal. The comb is a thin sheet of plastic, wood, or metal that separates the air chambers and channels the air. The reeds are metal plates that vibrate when air passes over them, producing the sound. The reeds are held in place by the reed plates. The mouthpiece is the part of the harmonica that you blow into to create sound. The buttons on the side of the harmonica control the air flow.
Types of Harmonicas
The harmonica is a versatile instrument, and many different types exist. The most common types are diatonic, chromatic, tremolo and octave harmonicas. Diatonic harmonicas are the most traditional and popular type, and are designed to produce a single key. Chromatic harmonicas are more complex and allow for a wider range of notes and provide more expressive options. Tremolo harmonicas use two reeds for each note, resulting in a vibrato effect. Octave harmonicas produce two notes for each hole, one in the standard octave and one an octave higher.
How Does a Harmonica Work?
- A harmonica is a small, rectangular instrument consisting of a series of metal reeds. Each reed is attached to a metal plate and is held in place by a thin metal frame.
- When the player blows into the instrument, the reeds vibrate, creating sound. The pitch of the sound depends on the length of the reed and how hard the player blows.
- The reeds are tuned to specific notes, usually in a scale, and a metal comb is used to divide the reeds into two groups – the lower and higher reeds.
- When the player presses a button, a metal slide is moved, allowing the air to flow through the reeds and create sound.
- The harmonica is a versatile instrument, and can produce a variety of sounds depending on how the player uses it. Different techniques such as bending, overblowing and vibrato can be used to create expressive and unique music.
The Physics of Sound Production
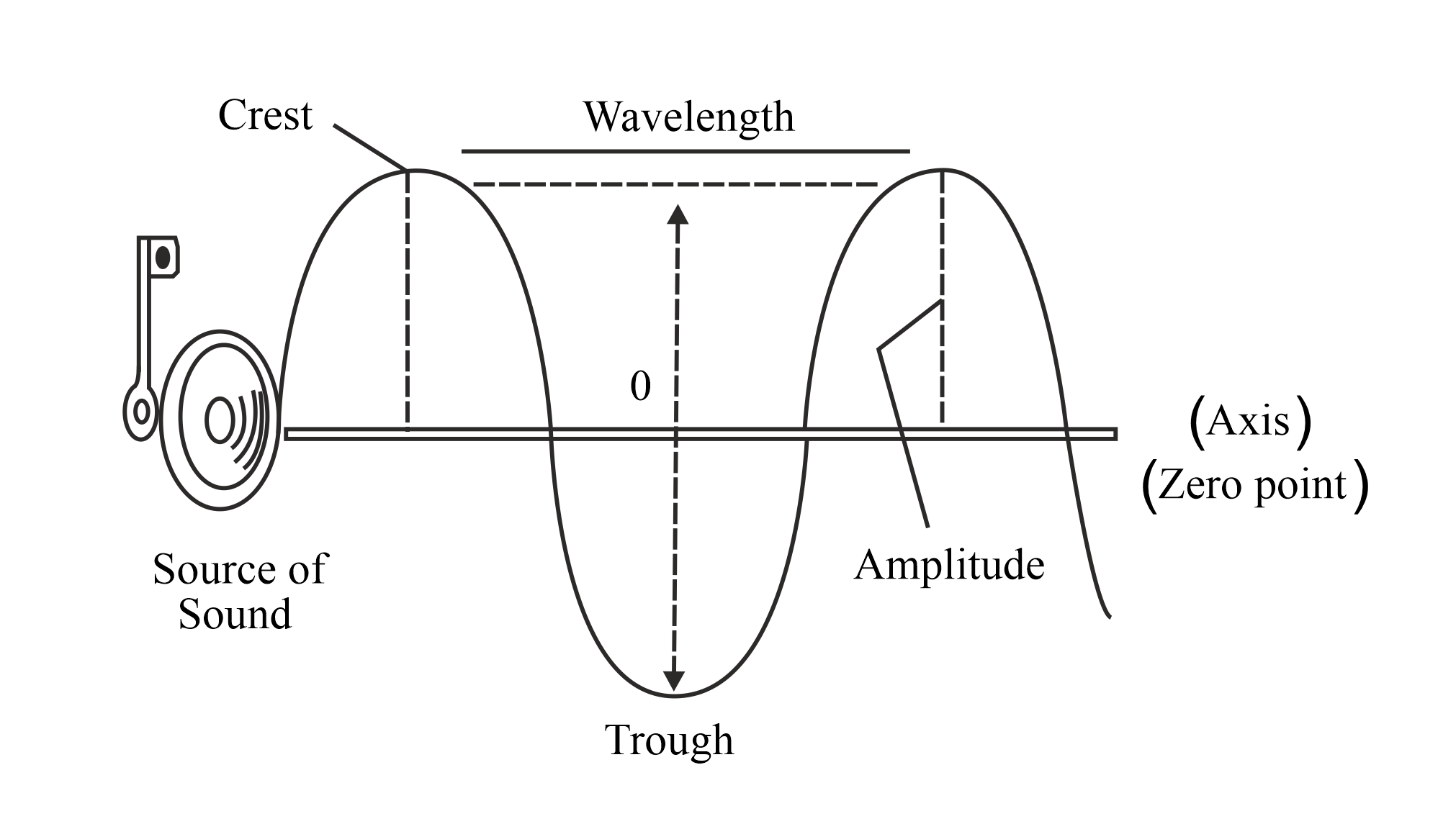
The sound of a harmonica is produced by the vibrations of its reeds. The reeds are metal tongues that are attached to the outside of the comb, the metal frame of the harmonica. When air is blown into the instrument, it vibrates the reeds which causes the sound waves to propagate through the air. The frequency of the reeds determines the pitch of the sound, and this is determined by the length and thickness of the reeds. The longer the reed, the lower the pitch, and the thicker the reed, the lower the pitch. The comb of the harmonica also affects the quality of the sound as it acts as a resonator, amplifying the sound waves and producing a fuller and brighter sound. In addition, the shape of the mouthpiece affects the sound as it determines the pressure and flow of air into the instrument.
Types of Harmonica Sounds
| Sound Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Chromatic | A harmonica played with a slide button allowing for a greater range of notes. |
| Diatonic | The most common type of harmonica, with a range of 7 notes per octave. |
| Tremolo | A harmonica that produces a vibrato effect by having two reeds per note. |
Harmonicas can produce several different types of sounds, depending on the type of instrument being used. Chromatic harmonicas are played with a slide button, allowing for a greater range of notes than the standard diatonic harmonica. Diatonic harmonicas are the most common type and are tuned to a range of 7 notes per octave. Tremolo harmonicas produce a vibrato effect by having two reeds per note.
How to Play the Harmonica
Playing the harmonica requires knowledge of the notes, understanding of embouchure, and a good sense of rhythm.
First, you must learn the notes of the harmonica. The harmonica is a diatonic instrument, meaning that it has a fixed set of notes. Each hole in the harmonica corresponds to a different note. It is important to memorize which note each hole produces, so that you can play songs that you already know.
Second, embouchure is the way the harmonica is held in your mouth. To play the harmonica correctly, you need to know how to form the correct embouchure. Your lips should form a seal around the harmonica, and your tongue should be placed inside the mouthpiece.
Finally, playing the harmonica requires a good sense of rhythm. You must be able to keep a steady tempo and be able to coordinate your breathing with the notes. It is also important to practice playing scales and learning songs to become more comfortable with the instrument.
With these tips, playing the harmonica will become easier and you will be able to enjoy the unique sound it produces.
Harmonica Music
Harmonica music is created by air passing through the instrument, causing the reeds to vibrate. This vibration is amplified by the instrument’s chambers, which are specially designed to produce the desired harmonica sound. The harmonica’s air chambers are divided into two parts: the blow chamber and the draw chamber. The blow chamber is used to produce sound when the player blows air through the harmonica, while the draw chamber is used to produce sound when the player draws air through the harmonica. The two chambers are separated by a thin wall, which prevents air from passing between them. This separation creates two distinct types of notes: the blow notes, which are created when air is blown through the blow chamber, and the draw notes, which are created when air is drawn through the draw chamber. By alternately blowing and drawing air through the harmonica, the player can create a melody. Each chamber also contains a series of reeds, which are made of metal or plastic, and are tuned to different pitches. The reeds vibrate when air passes through them, creating the harmonica’s distinctive sound.
Maintenance and Care of the Harmonica
Harmonicas are delicate instruments and need to be cared for properly to ensure the highest quality of sound. To maintain your harmonica, clean the reeds and comb regularly. Use a pipe cleaner to gently brush away any dust and debris from the reeds. Clean the comb with a soft cloth to remove any saliva residue. Also use a special harmonica lubricant to keep the reeds from sticking. The reeds should be checked every few months for wear and tear. If needed, replace any broken or worn reeds.
To protect your harmonica, store it in a safe and dry place away from extreme temperatures. A case is a great way to store and protect your harmonica in between uses. The harmonica should also be checked for any leaks or cracks. If there are any, repair them promptly to ensure optimal sound quality.
Finally, it is important to tune your harmonica regularly. This is done by replacing the reeds and adjusting the tuning screws. This should be done by a qualified technician to ensure the best sound quality.
Overall, proper maintenance and care of the harmonica is essential for optimal sound quality. Regular cleaning, tuning, and repair will help keep your harmonica sounding great for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the history of the Harmonica?
The harmonica is a small, free-reed wind instrument invented in the early 19th century. It was originally called the Mundharmonika in Germany, and was developed by Christian Friedrich Ludwig Buschmann in 1821. The harmonica was popular in Europe and America in the 19th and early 20th centuries, and was used in folk music, classical music, and popular music. The harmonica was also used in jazz, blues, and country music, and was popularized by blues and jazz musicians such as Little Walter, Sonny Boy Williamson, and Larry Adler. The harmonica has also been used in film scores and other forms of music. Today, the harmonica is still popular and is used in many different types of music.
How Does a Harmonica Work?
A harmonica is a free reed instrument that produces sound when air is blown across metal reeds. The metal reeds are mounted on a metal plate and connected to a metal cover by a spring. When air is blown across the metal reeds, they vibrate and produce a sound. The pitch of the sound is determined by the length of the reeds. The reeds can be bent to produce different notes, resulting in a range of musical sounds.
What techniques can be used to play the harmonica?
Playing the harmonica involves using various techniques such as blowing, drawing, overblowing, tongue blocking, and percussive effects. Blowing and drawing involves the player blowing air into the reeds or drawing air from the reeds, producing a sound. Overblowing is a technique where the player blows into the reeds in a way that creates a higher pitched note. Tongue blocking is when the player uses their tongue to block air from entering certain reeds while playing. Percussive effects involve the player hitting the harmonica as they play, creating a unique sound.
How is a harmonica different from other instruments?
A harmonica is a musical instrument consisting of a set of metal reeds, each mounted onto a metal comb and placed in a small rectangular box. Unlike other instruments, a harmonica is held in the player’s mouth and the sound is generated by blowing and/or drawing air over the reeds. The unique shape of the comb, with its air chambers and airtight covers, allows the air to be directed over the reeds, producing different notes. This feature makes the harmonica a versatile instrument, able to produce a variety of sounds, from single notes to chords and even full melodies.
What is the Unique Sound of the Harmonica?
The harmonica is a small, portable wind instrument that produces a distinctive sound when air is blown through reeds. Its sound is easily recognizable and has been featured in numerous genres of music, from folk and pop to blues, jazz, and rock. The harmonica’s sound is unique in that it can be both expressive and versatile, with a range of bright, lyrical tones and mellow, airy melodies. It also has a wide dynamic range, allowing it to play both loud and soft passages. Its portable size makes it a popular instrument for street performers, buskers, and blues musicians alike.
Conclusion
The harmonica is an iconic instrument that has been used for centuries. With its unique sound and versatility, it can create a wide range of musical styles and sounds. Its simple construction, portability, and affordability make it an ideal choice for anyone looking for a creative outlet. By understanding the science behind the harmonica and its components, the sound and potential of the instrument can be further explored. With an understanding of how the harmonica works, musicians will be able to create beautiful, unique music with this versatile instrument.